Classify the chemical changes as endothermic or exothermic. – Delving into the fascinating realm of chemical reactions, we embark on a journey to classify them as either endothermic or exothermic. This fundamental distinction, rooted in energy exchange, unveils the intricate interplay between chemical processes and their surroundings.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the defining characteristics of endothermic and exothermic reactions, unravel the energy changes that accompany them, and uncover the practical applications that harness their unique properties.
Definition of Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
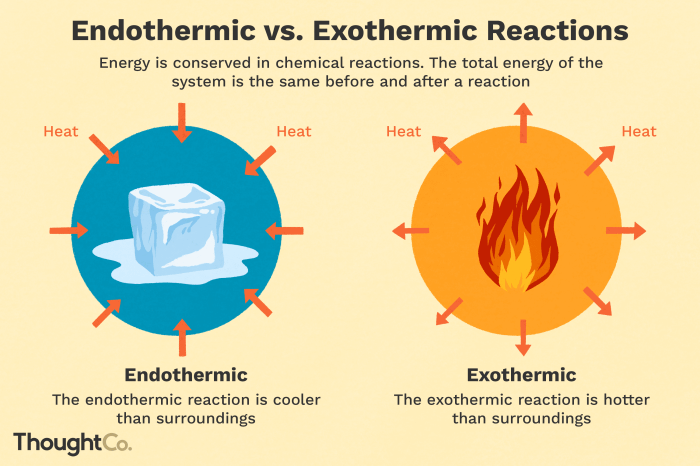
Chemical reactions involve changes in the energy of the reactants and products. Endothermic reactions are those that absorb energy from their surroundings, while exothermic reactions release energy into their surroundings.
Endothermic Reactions, Classify the chemical changes as endothermic or exothermic.
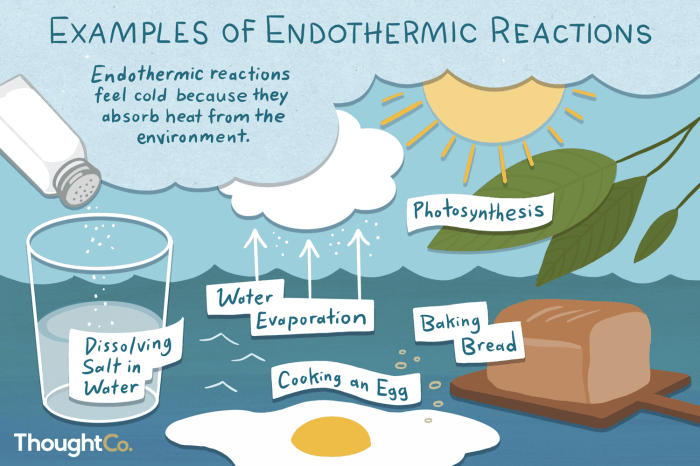
In endothermic reactions, the energy of the products is higher than the energy of the reactants. This means that energy must be supplied to the reaction in order for it to occur. Examples of endothermic reactions include photosynthesis, melting of ice, and sublimation of dry ice.
Exothermic Reactions
In exothermic reactions, the energy of the products is lower than the energy of the reactants. This means that energy is released from the reaction as it occurs. Examples of exothermic reactions include combustion, neutralization reactions, and the formation of ionic bonds.
Energy Changes in Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions

Energy Changes in Endothermic Reactions
In endothermic reactions, the energy change is positive. This means that the products have more energy than the reactants. The energy required for the reaction comes from the surroundings, which causes the temperature of the surroundings to decrease.
Energy Changes in Exothermic Reactions
In exothermic reactions, the energy change is negative. This means that the products have less energy than the reactants. The energy released by the reaction is transferred to the surroundings, which causes the temperature of the surroundings to increase.
Signs of Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Signs of Endothermic Reactions
- Temperature of the surroundings decreases.
- Heat is absorbed from the surroundings.
- The reaction mixture feels cold to the touch.
Signs of Exothermic Reactions
- Temperature of the surroundings increases.
- Heat is released into the surroundings.
- The reaction mixture feels hot to the touch.
- Light or flames may be produced.
Factors Affecting the Classification of Chemical Reactions as Endothermic or Exothermic
The enthalpy change of a reaction is the primary factor that determines whether it is classified as endothermic or exothermic. Enthalpy is a measure of the heat content of a system.
If the enthalpy change is positive, the reaction is endothermic. If the enthalpy change is negative, the reaction is exothermic.
Other factors that can affect the classification of a reaction include:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Concentration of reactants
- Presence of a catalyst
Applications of Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Applications of Endothermic Reactions
- Refrigeration
- Air conditioning
- Desalination
Applications of Exothermic Reactions
- Combustion engines
- Fireworks
- Explosives
Design an Experiment to Classify a Chemical Reaction as Endothermic or Exothermic
To classify a chemical reaction as endothermic or exothermic, you can design an experiment that measures the temperature change of the surroundings.
The following steps are involved in designing an experiment to classify a chemical reaction as endothermic or exothermic:
- Choose a chemical reaction to investigate.
- Set up an experimental apparatus that allows you to measure the temperature change of the surroundings.
- Carry out the reaction and record the temperature change.
- Analyze the results to determine whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
A detailed procedure for conducting the experiment can be found in a chemistry laboratory manual.
Create a Table Summarizing the Key Differences between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
| Characteristic | Endothermic Reactions | Exothermic Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Energy change | Positive | Negative |
| Temperature change of surroundings | Decreases | Increases |
| Heat flow | Heat absorbed from surroundings | Heat released into surroundings |
| Signs | Temperature of reaction mixture feels cold | Temperature of reaction mixture feels hot |
| Examples | Photosynthesis, melting of ice | Combustion, neutralization reactions |
FAQ Explained: Classify The Chemical Changes As Endothermic Or Exothermic.
What is the key difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions?
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, while exothermic reactions release energy into their surroundings.
How can I identify an endothermic reaction?
Signs of an endothermic reaction include a decrease in temperature, absorption of heat, and the need for an external energy source.
What are some practical applications of exothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions are used in a wide range of applications, including combustion engines, heating systems, and the production of fireworks.