Concentrated melanin cells on the face or body, medically known as hyperpigmentation, present an intriguing phenomenon that has captivated the attention of medical professionals and individuals alike. This condition, characterized by the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, can manifest in various forms, ranging from harmless freckles to more concerning medical conditions.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for concentrated melanin cells is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and preventing potential complications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this condition, providing valuable insights and practical advice.
Introduction
Concentrated melanin cells, also known as hyperpigmentation, occur when there is an increase in the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. This can result in the appearance of dark patches or spots on the face or body.
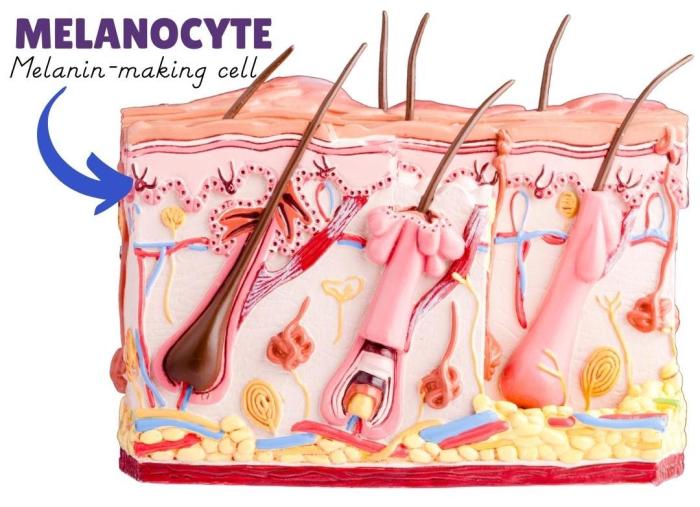
Melanin is produced by cells called melanocytes. When these cells are stimulated, they produce more melanin, which can lead to hyperpigmentation. The most common cause of concentrated melanin cells is sun exposure, but it can also be caused by hormonal changes, inflammation, or certain medications.
Types of Concentrated Melanin Cells
- Solar lentigines: These are flat, brown or black spots that are caused by sun exposure.
- Melasma: This is a condition that causes dark patches on the face, typically in women who are pregnant or taking birth control pills.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: This is a type of hyperpigmentation that occurs after an injury or inflammation to the skin.
Symptoms of Concentrated Melanin Cells
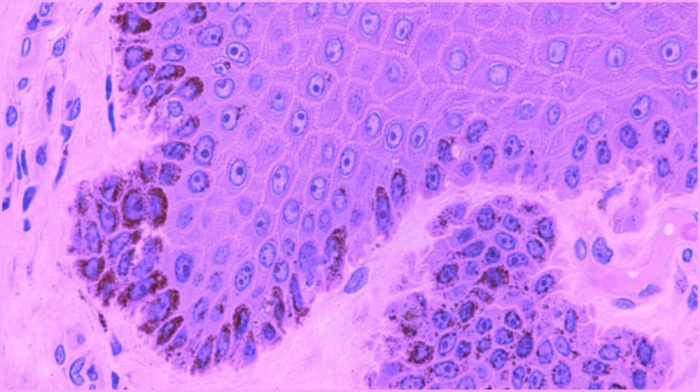
The most common symptom of concentrated melanin cells is the appearance of dark patches or spots on the skin. These patches can vary in size and shape, and they can be located anywhere on the body.
Other symptoms of concentrated melanin cells include:
- Itching or irritation
- Pain or tenderness
- Changes in skin texture
Differentiating Concentrated Melanin Cells from Other Skin Conditions
It is important to differentiate concentrated melanin cells from other skin conditions, such as skin cancer. Skin cancer can also cause dark patches or spots on the skin, but it is typically accompanied by other symptoms, such as bleeding, crusting, or changes in the size or shape of the spot.
If you are unsure whether a dark patch or spot on your skin is concentrated melanin cells or skin cancer, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis.
Risks and Complications of Concentrated Melanin Cells
Concentrated melanin cells are generally not harmful, but they can be a cosmetic concern. In some cases, concentrated melanin cells can also lead to complications, such as:
- Increased risk of skin cancer
- Scarring
- Infection
Diagnosis of Concentrated Melanin Cells
The diagnosis of concentrated melanin cells is typically based on a physical examination of the skin. Your doctor may also ask you about your medical history and any medications you are taking.
In some cases, your doctor may order a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of skin and examining it under a microscope.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of concentrated melanin cells is important to prevent complications, such as skin cancer and scarring.
Tests and Procedures for Diagnosing Concentrated Melanin Cells
- Physical examination
- Biopsy
- Wood’s lamp examination
- Dermoscopy
Treatment Options for Concentrated Melanin Cells: Concentrated Melanin Cells On The Face Or Body
There are a number of treatment options available for concentrated melanin cells. The best treatment option for you will depend on the type of hyperpigmentation you have, the severity of your condition, and your overall health.
Benefits and Risks of Each Treatment Option
| Treatment Option | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Topical treatments | – Can be used to lighten dark patches or spots | – May cause skin irritation or dryness |
| Laser therapy | – Can be used to remove dark patches or spots | – May cause skin redness or swelling |
| Chemical peels | – Can be used to remove dark patches or spots | – May cause skin redness or peeling |
| Microdermabrasion | – Can be used to remove dark patches or spots | – May cause skin redness or irritation |
Importance of Follow-up Care After Treatment
After treatment for concentrated melanin cells, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions for follow-up care. This may include using sunscreen, avoiding sun exposure, and using topical treatments to prevent the recurrence of hyperpigmentation.
Prevention of Concentrated Melanin Cells
There are a number of things you can do to prevent concentrated melanin cells, including:
Importance of Sun Protection, Concentrated melanin cells on the face or body
Sun exposure is the most common cause of concentrated melanin cells. To protect your skin from the sun, you should:
- Use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours
- Wear protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses
- Avoid sun exposure during peak hours (10am-4pm)
Other Ways to Prevent Concentrated Melanin Cells
- Avoid hormonal changes
- Avoid inflammation
- Avoid certain medications
FAQ Explained
What are the common causes of concentrated melanin cells?
Sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and certain medications can all contribute to the formation of concentrated melanin cells.
How can I differentiate between concentrated melanin cells and other skin conditions?
Concentrated melanin cells typically appear as dark patches on the skin, while other conditions may have different symptoms such as redness, scaling, or itching. A dermatologist can help with accurate diagnosis.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with concentrated melanin cells?
While most concentrated melanin cells are benign, some types can develop into skin cancer if left untreated. It’s important to have any changes in skin pigmentation evaluated by a healthcare professional.