Delving into the realm of electromagnetic waves, this comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of these ubiquitous phenomena, encompassing their nature, properties, applications, and safety considerations. Electromagnetic waves sum it up answer key unravels the mysteries of these waves, providing a thorough understanding of their impact on our world.
Electromagnetic waves, the messengers of our technological age, permeate every aspect of our lives, from the communication networks that connect us to the medical imaging that heals us. Understanding their fundamental properties and applications empowers us to harness their potential and navigate their potential risks.
Electromagnetic Waves: Electromagnetic Waves Sum It Up Answer Key
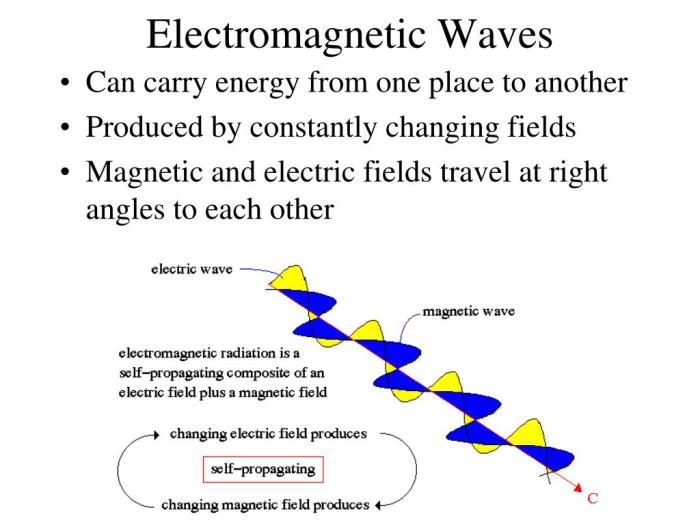
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that propagates through space and matter. They are characterized by their electric and magnetic fields, which oscillate perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation.
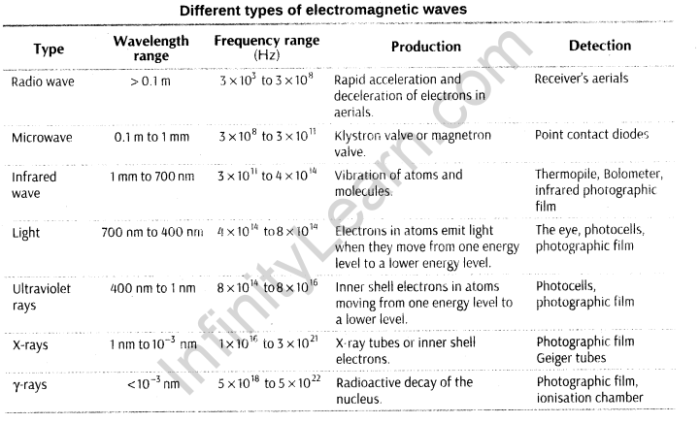
Electromagnetic waves form a continuous spectrum, ranging from extremely low frequencies (ELF) to extremely high frequencies (EHF). Different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum have distinct properties and applications.
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
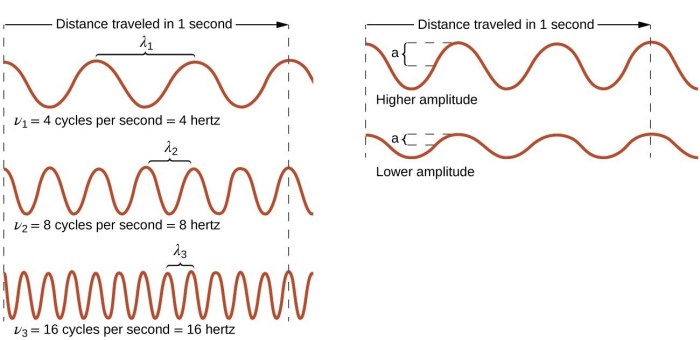
- Frequency: The number of oscillations per second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Wavelength: The distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave, measured in meters (m).
- Amplitude: The maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position, measured in volts (V) or meters (m).
These properties determine the behavior of electromagnetic waves, such as their energy, penetration depth, and interaction with matter.
Generation and Detection of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves can be generated using various methods, including antennas and transmitters. Antennas convert electrical signals into electromagnetic waves, while transmitters amplify and broadcast the waves.
Electromagnetic waves can be detected using devices such as receivers and detectors. Receivers pick up the waves and convert them into electrical signals, while detectors measure the intensity or frequency of the waves.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves, Electromagnetic waves sum it up answer key
- Communication: Electromagnetic waves are used for wireless communication, including cell phones, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication.
- Navigation: Electromagnetic waves are used in navigation systems such as GPS and radar.
- Medical Imaging: Electromagnetic waves are used in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound.
- Scientific Research: Electromagnetic waves are used in scientific research, including astronomy, spectroscopy, and material characterization.
Safety Considerations
Exposure to high levels of electromagnetic waves can have potential health effects. Guidelines and regulations have been established to limit exposure to harmful levels of radiation.
It is recommended to use devices that emit electromagnetic waves in moderation and to follow safety guidelines to minimize potential health risks.
FAQs
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What are the properties of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are characterized by their frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. Frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point in one second, wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave, and amplitude is the height of a wave.
What are the applications of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are used in a wide variety of applications, including communication, navigation, medical imaging, and scientific research.
What are the safety considerations for electromagnetic waves?
Exposure to high levels of electromagnetic radiation can be harmful to human health. However, the levels of electromagnetic radiation emitted by most devices are well below the safety limits.