Delve into the fascinating realm of chemistry with our comprehensive Periodic Table Basics Worksheet Answers, where the periodic table unravels its secrets, revealing the fundamental principles that govern the elements and their interactions. This in-depth resource provides a thorough understanding of the periodic table’s organization, properties, and applications, empowering you to master the intricacies of chemistry.
From the historical roots of the periodic table to its modern-day significance, we explore the fascinating journey of this scientific masterpiece. Discover the periodic trends that shape the properties of elements, unravel the mysteries of chemical bonding, and witness the practical applications that make the periodic table an indispensable tool in various scientific disciplines.
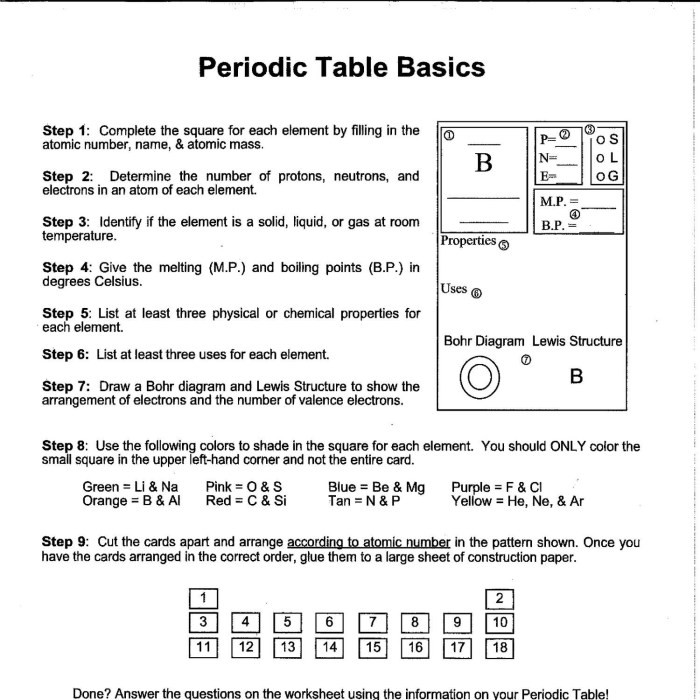
Introduction to the Periodic Table: Periodic Table Basics Worksheet Answers
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It was first developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, and has since become an essential tool for chemists and other scientists.
The periodic table is divided into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right, and the periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom.
Elements and Their Properties
Elements are the basic building blocks of matter. They are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
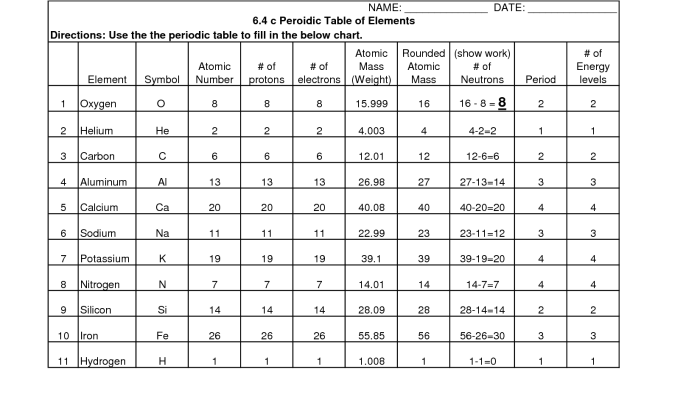
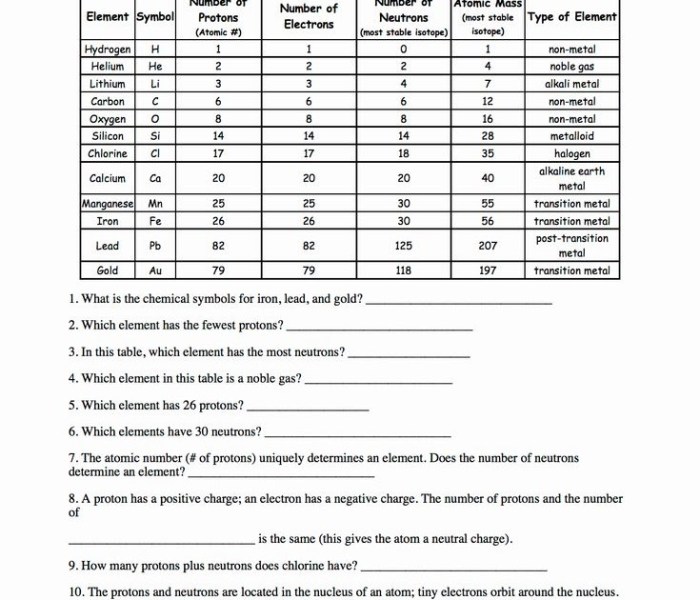
Each element is identified by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. The atomic number also determines the element’s position on the periodic table.
The elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. This arrangement reveals periodic trends in the elements’ properties.
Groups and Periods
The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups. The elements in a group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons.
The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The elements in a period have the same number of electron shells.
The group number of an element indicates the number of valence electrons it has. The period number of an element indicates the number of electron shells it has.
Chemical Bonding, Periodic table basics worksheet answers
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms join together to form molecules and compounds.
There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
The type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms depends on the electronegativity of the atoms.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a powerful tool that can be used to predict the properties of elements and compounds.
The periodic table can be used to:
- Predict the chemical properties of an element based on its position on the table.
- Identify the elements that are most likely to form compounds with each other.
- Design new materials with specific properties.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
What are the main groups and periods in the periodic table?
The periodic table consists of 18 vertical columns, known as groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. Elements within the same group share similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
How does the periodic table help predict chemical behavior?
The position of an element on the periodic table provides valuable insights into its chemical reactivity, bonding preferences, and physical properties. By understanding the periodic trends, chemists can make informed predictions about the behavior of elements and their compounds.